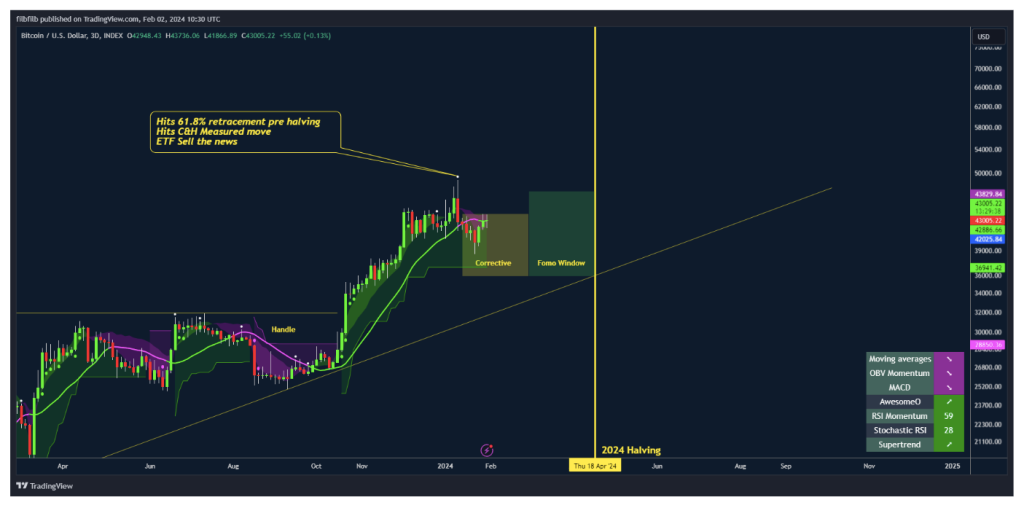
As the countdown to the highly anticipated Bitcoin halving enters its final stretch, the cryptocurrency market is experiencing a surge in inflows to Bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs). With less than 60 days remaining until the halving event, investors are eyeing the potential for a demand shock rally in Bitcoin, fueled by dwindling supply and increasing institutional interest.
Rising Inflows to Bitcoin ETFs: In recent weeks, Bitcoin ETFs have witnessed a significant uptick in investor demand, reflecting growing confidence in the long-term potential of the digital asset. Institutional investors, in particular, are increasingly turning to Bitcoin ETFs as a convenient and regulated way to gain exposure to the cryptocurrency market. The influx of capital into these investment vehicles signals a broader acceptance of Bitcoin as a legitimate asset class and underscores its growing prominence in the global financial landscape.
The Bitcoin Halving: A Catalyst for Price Appreciation: Scheduled to occur approximately every four years, the Bitcoin halving is an event programmed into the cryptocurrency’s protocol that reduces the reward miners receive for validating transactions by half. This scarcity mechanism is designed to control inflation and ensure a predictable and finite supply of Bitcoin. Historically, each halving event has been accompanied by a surge in Bitcoin’s price, as the reduction in new supply creates upward pressure on its value. With the next halving set to occur in less than 60 days, anticipation is mounting among investors, who view it as a potential catalyst for a demand-driven rally in Bitcoin.
Demand Shock Rally: A demand shock rally occurs when a sudden increase in demand overwhelms existing supply, leading to a rapid appreciation in price. In the context of Bitcoin, the combination of institutional adoption, dwindling supply due to the halving, and increasing retail interest has the potential to trigger such a rally. As more investors seek exposure to Bitcoin as a hedge against economic uncertainty and inflationary pressures, the cryptocurrency’s scarcity value is expected to drive prices higher in the coming months.
Key Considerations: While the prospect of a demand shock rally in Bitcoin is enticing, investors should exercise caution and consider several key factors. Market volatility, regulatory uncertainty, and the evolving macroeconomic landscape can all impact the trajectory of Bitcoin’s price. Additionally, the long-term viability of Bitcoin as a store of value and medium of exchange remains a subject of debate among economists and market participants.
As the countdown to the Bitcoin halving continues, the cryptocurrency market is brimming with anticipation and excitement. The surge in inflows to Bitcoin ETFs suggests that institutional investors are positioning themselves for potential upside in Bitcoin’s price. While the halving event is widely expected to be a bullish catalyst for Bitcoin, investors should remain vigilant and carefully assess the risks and opportunities associated with investing in the cryptocurrency market. As the digital asset ecosystem continues to mature, Bitcoin’s role as a viable alternative investment is likely to become increasingly pronounced in the years ahead.
The History of Bitcoin Halving and Price Appreciation
Bitcoin halving events have long been anticipated by cryptocurrency enthusiasts and investors alike due to their significant impact on the digital currency’s supply and price dynamics. Since Bitcoin’s inception, halving events have played a crucial role in shaping its price trajectory and garnering attention from the broader financial community. Here’s a brief history of Bitcoin halving events and their correlation with price appreciation:
1. Genesis Block and the First Halving (2012): Bitcoin was created by an anonymous individual or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto, who mined the genesis block on January 3, 2009. The first Bitcoin halving occurred on November 28, 2012, when the block reward was reduced from 50 BTC to 25 BTC per block. This event marked a significant milestone in Bitcoin’s history, as it effectively reduced the rate at which new Bitcoins were introduced into circulation. Following the first halving, Bitcoin’s price experienced a substantial rally, reaching new all-time highs in the years that followed.
2. Second Halving (2016): The second Bitcoin halving took place on July 9, 2016, reducing the block reward from 25 BTC to 12.5 BTC. Leading up to the halving, there was considerable speculation and anticipation among investors regarding its potential impact on Bitcoin’s price. In the months following the event, Bitcoin’s price began to surge, ultimately reaching an all-time high of nearly $20,000 in December 2017. The second halving solidified Bitcoin’s reputation as a deflationary digital asset and reinforced its appeal as a store of value.
3. Third Halving (2020): The most recent Bitcoin halving occurred on May 11, 2020, reducing the block reward from 12.5 BTC to 6.25 BTC. Similar to previous halving events, the third halving was met with heightened anticipation and speculation from investors and analysts. In the months leading up to the halving, Bitcoin’s price experienced significant volatility, with many investors positioning themselves for potential price appreciation following the event. Following the halving, Bitcoin’s price experienced a gradual uptrend, eventually surpassing its previous all-time high in December 2020 and continuing to climb to new heights in 2021.
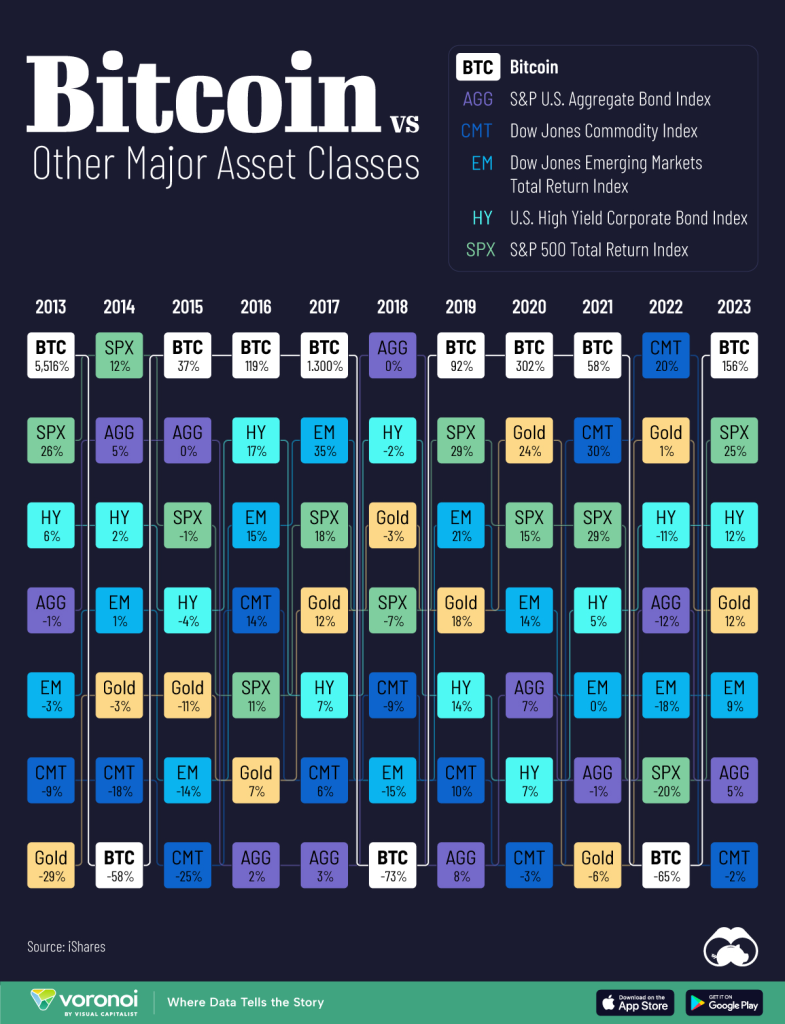
Correlation with Price Appreciation: Historically, Bitcoin halving events have been associated with periods of price appreciation and bullish sentiment in the cryptocurrency market. The reduction in the rate of new supply issuance, combined with growing demand from investors and institutions, has contributed to significant price rallies following each halving. Additionally, the scarcity narrative surrounding Bitcoin has been reinforced by halving events, further bolstering its value proposition as a hedge against inflation and macroeconomic uncertainty.
Bitcoin halving events have emerged as pivotal milestones in the cryptocurrency’s history, signaling a maturation of its monetary policy and supply dynamics. With each halving, Bitcoin’s scarcity and value proposition are accentuated, leading to heightened interest from investors and increased price appreciation. As Bitcoin continues to gain mainstream acceptance and adoption, halving events are expected to remain key catalysts for future price growth and market dynamics in the evolving digital asset ecosystem.
The Bitcoin halving event has a direct impact on the supply of Bitcoin by reducing the rate at which new Bitcoins are created and introduced into circulation. Here’s how the halving affects the supply of Bitcoin:
- Reduction in Block Rewards: Bitcoin miners are rewarded with a certain number of Bitcoins for validating and adding new transactions to the blockchain. The halving event cuts the block reward in half, effectively reducing the number of new Bitcoins generated with each mined block. For example, in the most recent halving event in May 2020, the block reward was reduced from 12.5 BTC to 6.25 BTC.
- Decreased Rate of Supply Inflation: By halving the block rewards, the rate of supply inflation of Bitcoin decreases. This means that the pace at which new Bitcoins are created slows down significantly. As a result, the total supply of Bitcoin grows at a diminishing rate over time, approaching its maximum limit of 21 million Bitcoins.
- Scarcity and Increased Demand: Bitcoin is often compared to gold due to its scarcity and limited supply. The halving events reinforce Bitcoin’s scarcity narrative, as the reduced rate of new supply issuance makes it increasingly difficult to acquire new Bitcoins. This scarcity, combined with growing demand from investors and institutions, tends to drive up the price of Bitcoin over the long term.
- Market Dynamics and Price Impact: The reduction in the rate of new supply issuance can lead to supply-demand imbalances in the market, potentially contributing to upward pressure on Bitcoin’s price. Historically, Bitcoin halving events have been associated with periods of significant price appreciation and bullish sentiment as investors anticipate the impact of reduced supply inflation on the asset’s value.
The Bitcoin halving event directly affects the supply dynamics of Bitcoin by reducing the rate at which new coins are created. This reduction in new supply issuance, combined with increasing demand, tends to reinforce Bitcoin’s scarcity narrative and has historically led to periods of price appreciation in the cryptocurrency market.
Bitcoin, the world’s first decentralized cryptocurrency, was introduced in 2009 by an unknown person or group of people using the pseudonym “Satoshi Nakamoto.” Since its inception, Bitcoin has transformed the landscape of finance and technology, revolutionizing the way people think about money and digital transactions. Here’s a brief history of Bitcoin:
- Inception (2008-2009): The concept of Bitcoin was first outlined in a whitepaper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System,” published by Satoshi Nakamoto in October 2008. The following year, on January 3, 2009, Nakamoto mined the first block of the Bitcoin blockchain, known as the “genesis block,” marking the official launch of the Bitcoin network.
- Early Development (2009-2010): In the early days, Bitcoin had little monetary value, and mining could be done with basic computer hardware. The first known commercial transaction involving Bitcoin occurred in May 2010 when Laszlo Hanyecz famously purchased two pizzas for 10,000 BTC, establishing the first real-world value of Bitcoin.
- Early Adoption and Growth (2011-2013): Bitcoin gained traction among tech enthusiasts, libertarians, and early adopters who saw its potential as a decentralized currency. The price of Bitcoin remained relatively low until 2013 when it experienced its first major price rally, reaching over $1,000 for the first time in November.
- Volatility and Mt. Gox (2014-2015): Despite its growing popularity, Bitcoin faced challenges, including price volatility and security concerns. The most significant setback during this period was the collapse of Mt. Gox, one of the largest Bitcoin exchanges at the time, in early 2014 due to hacking and insolvency, resulting in the loss of hundreds of millions of dollars worth of Bitcoin.
- Maturation and Mainstream Recognition (2016-2017): Bitcoin continued to gain mainstream recognition and acceptance, with growing interest from institutional investors and financial institutions. The price of Bitcoin surged to new highs in late 2017, reaching almost $20,000 in December, driven by speculative trading and media attention.
- Regulatory Scrutiny and Market Correction (2018-2019): The rapid price increase in 2017 was followed by a sharp correction in 2018, with Bitcoin losing over 80% of its value from its peak. Regulatory scrutiny increased, particularly regarding initial coin offerings (ICOs) and cryptocurrency exchanges, leading to a more cautious approach from governments and regulators worldwide.
- Bitcoin Halving (2020): In May 2020, Bitcoin experienced its third “halving” event, reducing the block reward from 12.5 BTC to 6.25 BTC. This event, programmed into the Bitcoin protocol, reduces the rate of new Bitcoin issuance and is often associated with long-term price appreciation due to increased scarcity.
- Institutional Adoption and Price Surge (2020-2021): Institutional interest in Bitcoin grew significantly in 2020, with companies like MicroStrategy and Square investing substantial sums of money in Bitcoin as a hedge against inflation. This trend continued into 2021, culminating in Bitcoin reaching a new all-time high above $60,000 in April.
- Market Correction and Regulatory Developments (2021-Present): Following its peak in April 2021, Bitcoin experienced a significant price correction, driven by factors such as regulatory concerns, environmental issues related to Bitcoin mining, and increased market volatility. Despite these challenges, Bitcoin remains a dominant force in the cryptocurrency market, with ongoing developments in technology, regulation, and adoption shaping its future trajectory.
Overall, the history of Bitcoin is characterized by innovation, volatility, and resilience, with its impact extending far beyond the realm of finance into areas such as technology, economics, and politics. As the world continues to adapt to the digital age, Bitcoin continues to play a central role in shaping the future of money and decentralized finance.
Shayne Heffernan









