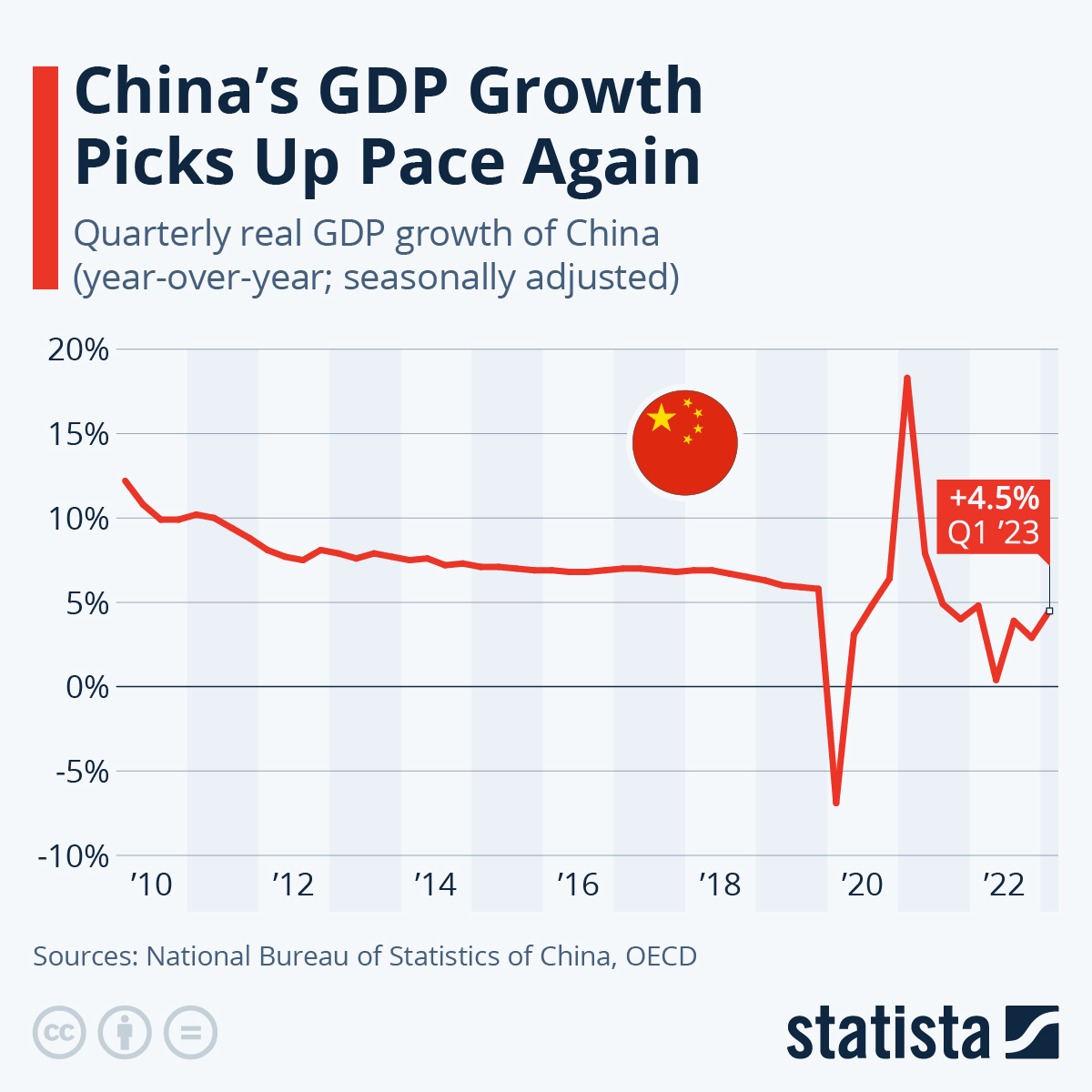
China fully resumed normal social and economic operation in April, with multiple output and demand indicators registering faster growth, indicating continued upward momentum in economic performance.
Last month, the world’s second-largest economy saw a steady expansion in industrial output, consumption and the services sector, among others, data from the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) showed Tuesday.
The value-added industrial output went up 5.6 percent year on year, 1.7 percentage points higher than that of March.
In particular, the production of new-energy automobiles and solar cells surged 85.4 percent and 69.1 percent year on year, respectively.
The retail sales of consumer goods, a major indicator of the country’s consumption strength, surged 18.4 percent year on year to nearly 3.5 trillion yuan (about 503 billion U.S. dollars).
The country’s production index of the services sector rose 13.5 percent year on year last month, 4.3 percentage points faster than that of March.
In the first four months, fixed-asset investment rose 4.7 percent year on year to 14.75 trillion yuan, with investment in high-tech manufacturing and services increasing 15.3 percent and 13.4 percent, respectively.
While major economic indicators have pointed to sustained economic development, the NBS spokesperson Fu Linghui warned of challenges including the complex international situation and insufficient domestic demand.
Looking forward, China will expand demand, accelerate the development of a modern industrial system, and work hard to promote high-quality economic development, said Fu.
China is one of the most important countries in the global economy today. With a population of over 1.4 billion people and an economy that has grown rapidly over the past few decades, China has become a major player in the world’s economic landscape. In this article, we will explore the reasons why China is so important to the global economy.
First and foremost, China is the world’s second-largest economy after the United States. Its gross domestic product (GDP) in 2021 was estimated to be over $16 trillion, and it is expected to continue growing in the coming years. China’s economic growth has been fueled by a number of factors, including its massive population, low labor costs, and extensive infrastructure.
China is also one of the world’s largest exporters, with a vast array of products that are shipped to markets around the world. The country is a leading exporter of goods such as electronics, textiles, machinery, and chemicals. Its export market has grown rapidly over the past few decades, and today China is the world’s largest trading nation.
China’s importance in the global economy is further highlighted by its role in global supply chains. Many of the products that are manufactured in China are used in the production of goods by other countries. For example, Chinese-made components are used in the manufacture of iPhones, which are then sold around the world. As a result, disruptions to China’s manufacturing sector can have ripple effects throughout the global economy.
Another reason why China is important to the global economy is its role as a major creditor nation. China holds a large amount of foreign currency reserves, which it uses to invest in other countries’ debt. This gives China significant influence in global financial markets and allows it to exert economic leverage in international affairs.
Finally, China’s importance in the global economy is underscored by its participation in international organizations such as the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF). China is a major player in these organizations and has used its influence to push for greater representation of developing countries in global economic decision-making.
China will continue to be an important player in the global economy for the foreseeable future. Its economic power and influence will continue to shape the world’s economic landscape and affect the fortunes of countries around the globe.
Shayne Heffernan