Nuclear Power and the Surge in Demand for Uranium: A Comprehensive Overview
As the global energy landscape undergoes significant shifts towards sustainable and clean alternatives, the demand for nuclear power has seen a resurgence. Uranium, a key component in nuclear fuel, is witnessing increased attention and investment. This article delves into the rising demand for uranium and provides a handy table of uranium miners listed in the USA.
The Resurgence of Nuclear Power:
- Growing Energy Needs: With the escalating demand for energy worldwide, nuclear power is regaining favor as a reliable and low-carbon energy source.
- Emission Reduction Goals: Many countries are turning to nuclear power to meet their carbon reduction targets, as it offers a stable and large-scale energy supply without emitting greenhouse gases.
- Advanced Reactor Technologies: Advancements in nuclear reactor technologies are making them safer, more efficient, and economically viable, further contributing to the renewed interest in nuclear energy.
In the global pursuit of sustainable energy solutions, nuclear power stands out as a powerful and efficient source that can play a crucial role in meeting the rising demand for electricity while minimizing environmental impact. This article explores the attributes that make nuclear power a compelling option for a sustainable energy future.
- Low Carbon Emissions: Nuclear power plants generate electricity without emitting large amounts of greenhouse gases. Unlike fossil fuels, nuclear energy produces electricity without relying on the combustion process, making it a low-carbon energy source.
- High Energy Density: Nuclear power has an incredibly high energy density. A small amount of uranium fuel can produce a substantial amount of electricity, making nuclear power plants efficient and capable of meeting the energy demands of large populations.
- Continuous Power Generation: Nuclear power plants provide a stable and continuous source of electricity. Unlike some renewable energy sources that depend on weather conditions, nuclear reactors can operate continuously, ensuring a consistent power supply.
- Reduced Land Footprint: Nuclear power requires significantly less land compared to certain renewable energy sources like solar or wind farms. Nuclear plants can produce large amounts of electricity in a relatively small area, making them suitable for locations with limited space.
- Base Load Power Source: Nuclear power serves as a reliable base load power source, meaning it can consistently generate electricity to meet the minimum demand. This stability complements the intermittent nature of some renewable sources, contributing to a balanced energy grid.
- Technological Advancements: Ongoing advancements in nuclear reactor designs, safety protocols, and waste management technologies are enhancing the overall sustainability and safety of nuclear power.
- Decades of Proven Experience: Nuclear power has been successfully utilized for decades, providing a reliable and well-established source of energy in many countries. This extensive experience contributes to the confidence in the safety and efficacy of nuclear power.
Uranium Miners in the USA: Here is a table of notable uranium mining companies listed in the USA:
| Company Name | Ticker Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cameco Corporation | CCJ | Leading global uranium producer |
| Energy Fuels Inc. | UUUU | Engaged in uranium and vanadium production |
| Denison Mines Corp. | DNN | Focused on uranium exploration and mining |
| Uranium Energy Corp. | UEC | Involved in uranium mining and exploration |
| Peninsula Energy | PENMF | Australian-based company with US uranium assets |
Note: This table is not exhaustive, and investors are advised to conduct thorough research before making any investment decisions.
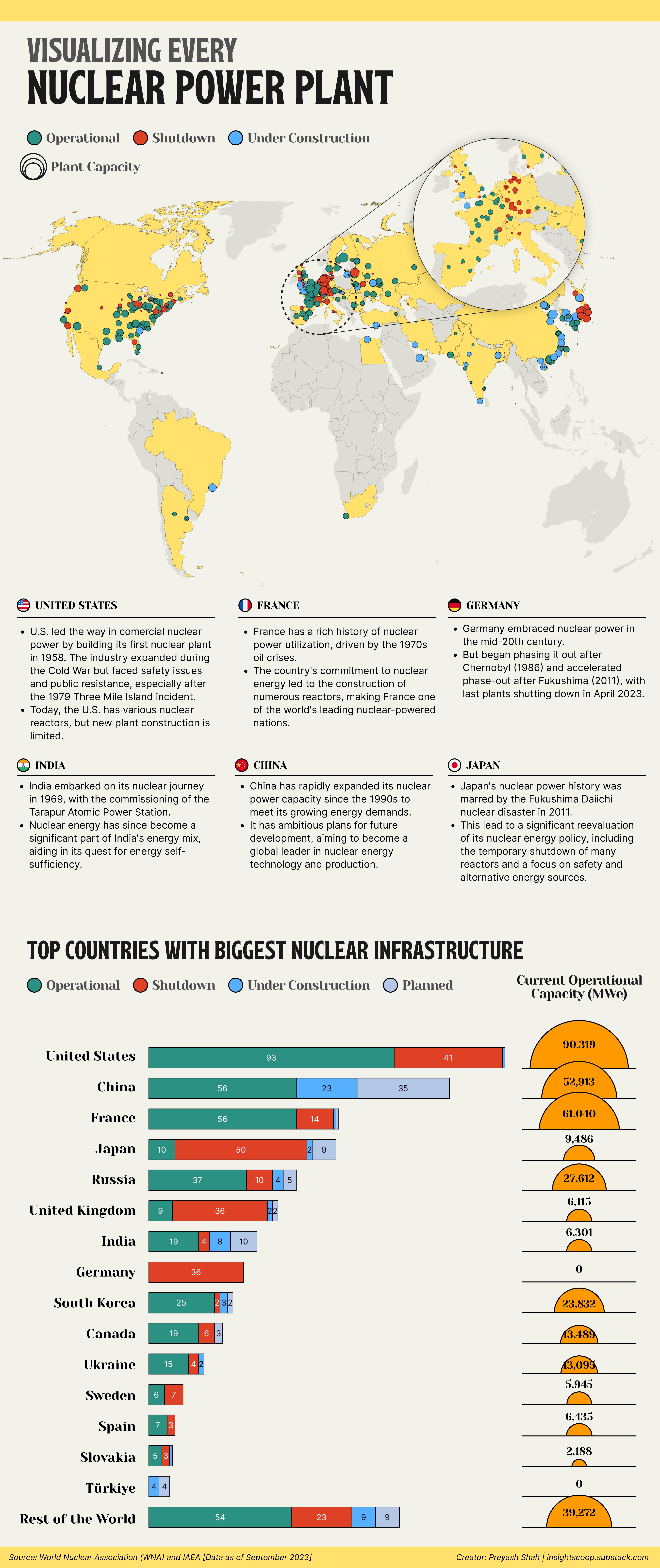
A comparative analysis, focusing on nuclear power and its key counterparts to understand their strengths and weaknesses in the pursuit of sustainable energy.
- Nuclear vs. Fossil Fuels:
- Carbon Emissions: Nuclear produces electricity with minimal greenhouse gas emissions, presenting a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels.
- Resource Depletion: Unlike finite fossil fuel reserves, nuclear energy relies on uranium, a more abundant resource.
- Nuclear vs. Renewable Energy:
- Reliability: Nuclear provides a continuous and reliable source of electricity, addressing intermittency concerns associated with some renewables.
- Land Use: Nuclear plants require less land compared to expansive solar or wind farms, making them suitable for regions with space constraints.
- Nuclear vs. Solar Power:
- Energy Density: Nuclear boasts a significantly higher energy density than solar power, enabling the production of large amounts of electricity in a smaller footprint.
- Intermittency: Solar power depends on sunlight availability, making it less consistent compared to nuclear energy.
- Nuclear vs. Wind Power:
- Space Efficiency: Nuclear plants require less land than expansive wind farms, particularly advantageous in densely populated areas.
- Wind Variability: Nuclear provides stable energy output, unlike wind power, which is subject to fluctuations in wind intensity.
- Nuclear vs. Hydroelectric Power:
- Environmental Impact: While both sources are considered low-carbon, hydroelectric power may have significant environmental consequences, such as altering river ecosystems and causing habitat disruptions.
- Geographical Limitations: Hydroelectric plants are location-dependent, requiring suitable water resources, whereas nuclear plants can be established in diverse environments.
- Nuclear vs. Geothermal Power:
- Geographical Accessibility: Nuclear power is not constrained by geographical locations, offering flexibility in plant placement, whereas geothermal power is geographically limited.
- Land Use: Geothermal plants may require extensive land use, while nuclear plants can produce substantial energy in a relatively small area.
Factors Driving Uranium Demand:
- Nuclear Energy Expansion: The construction and planning of new nuclear power plants globally are contributing to increased uranium demand.
- Supply Chain Concerns: The uranium supply chain has faced challenges, including mine closures and underinvestment, intensifying the need for new sources.
- Government Support: Some governments are actively supporting the development of nuclear power, providing incentives and regulatory frameworks to promote the industry.
As the world navigates the transition to cleaner and sustainable energy, uranium’s role in the nuclear power sector is gaining prominence. Investors and stakeholders are closely monitoring the uranium market, considering the potential for growth and the vital role nuclear energy may play in the future energy mix.

Powering the Future: The Growing Need for Electricity
Electricity is the lifeblood of the modern world. It illuminates our homes, fuels our industries, and connects us to information and entertainment. As our reliance on technology grows, so too does our demand for this vital resource. In this article, we’ll explore the factors driving the increasing need for electricity and examine the challenges and opportunities this presents.
Factors Fueling the Demand:
- Population Growth: A burgeoning global population translates to more homes, businesses, and devices requiring electricity. By 2050, the world’s population is projected to reach 9.7 billion, further straining existing electricity grids.
- Urbanization: The migration of people to cities concentrates energy demands, putting pressure on urban infrastructure. Megacities, with their high-rise buildings and complex transportation systems, are particularly dependent on reliable electricity supplies.
- Economic Development: As developing countries experience economic growth, their energy needs soar. This includes increasing demand for electricity for manufacturing, infrastructure development, and improved living standards.
- Technological Advancements: The proliferation of electronic devices, from smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles and smart homes, is significantly increasing household energy consumption. Additionally, advancements in industries like data centers and artificial intelligence further contribute to the growing demand.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The growing need for electricity presents both challenges and opportunities. On the one hand, we need to ensure sufficient generation capacity to meet the rising demand without relying on unsustainable or environmentally damaging sources like fossil fuels. On the other hand, this presents an opportunity to invest in clean energy technologies like Nuclear power, contributing to the fight against climate change and creating new jobs and economic growth.
Several countries around the world possess significant uranium deposits, playing crucial roles in the global uranium mining industry. Some of the countries with large uranium deposits include:
- Kazakhstan:
- Home to some of the world’s largest uranium deposits.
- The country has become a major player in global uranium production.
- Canada:
- Has substantial uranium resources, particularly in the Athabasca Basin in Saskatchewan.
- Uranium mining is a significant industry in Canada.
- Australia:
- Holds some of the world’s largest uranium reserves.
- Has active uranium mines, contributing to global supply.
- Namibia:
- Rich uranium deposits, with the Husab Mine being one of the largest uranium mines globally.
- Niger:
- A major uranium producer in Africa, with significant reserves.
- Russia:
- Possesses considerable uranium resources, and uranium mining is part of its energy strategy.
- Uzbekistan:
- Has significant uranium deposits and is actively involved in uranium mining.
- United States:
- Historically a significant producer, with uranium resources found in various states.
- China:
- Growing importance in the global uranium market, with increasing domestic production.
- Malawi:
- Emerging as a player in the uranium industry, with known deposits.
These countries contribute to the global uranium supply, playing essential roles in meeting the demands of nuclear power generation and other applications. It’s important to note that the availability and accessibility of uranium deposits can change over time due to exploration, technological advancements, and geopolitical factors.
Shayne Heffernan









