In the heart of China’s economic powerhouse, Beijing’s real estate market stands as a reflection of the city’s vibrant culture, economic strength, and urban evolution. As the capital city, Beijing’s real estate landscape has witnessed remarkable growth and transformation, becoming a focal point for investors, residents, and policymakers alike. In this exploration, we delve into the intricacies of Beijing’s real estate market, examining key trends, factors shaping its trajectory, and the significance of its role in the broader economic context.
The Evolution of Beijing’s Real Estate Market
Beijing’s real estate journey is one marked by rapid urbanization and dynamic economic growth. Over the past few decades, the city has seen a significant shift from traditional courtyard homes to towering skyscrapers and modern residential complexes. The demand for real estate in Beijing has been primarily driven by factors such as population growth, urban migration, and the city’s status as a political, cultural, and economic hub.
Residential Real Estate: A High-Stakes Arena
Graph: Beijing Residential Property Price Index (2010-2023)
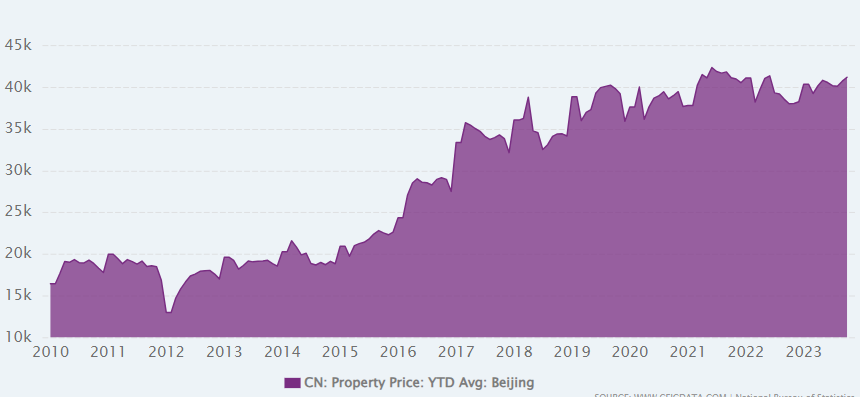
The Residential Property Price Index (RPPI) serves as a barometer for the health of Beijing’s residential real estate market. The graph illustrates the trajectory of property prices from 2010 to 2023, showcasing the market’s fluctuations, peaks, and plateaus.
As evident in the graph, Beijing’s residential property market has experienced notable volatility. The steep ascent in the early 2010s mirrors the city’s economic boom and increasing urbanization. Subsequent plateaus and dips reflect periods of regulatory interventions, aimed at curbing speculative behavior and maintaining market stability.
Government Policies and Market Dynamics
Beijing’s real estate market is not immune to government interventions and policy shifts. Chinese authorities have implemented a series of measures to regulate the property market, control housing prices, and address concerns about affordability. Policies such as purchase restrictions, increased down payment requirements, and lending rate adjustments have been employed to balance market forces and maintain stability.
The government’s focus on promoting a long-term, stable real estate market is evident in initiatives like the “Housing Provident Fund,” designed to help residents with down payments and mortgage rates. Additionally, efforts to encourage rental housing development align with a broader vision for a diversified and sustainable real estate landscape.
Commercial Real Estate: Navigating the Business Hub
Beyond residential properties, Beijing’s commercial real estate sector is a thriving hub for businesses and investors. The Central Business District (CBD), with its iconic skyline dominated by skyscrapers, is a testament to the city’s economic vitality. The demand for premium office spaces, retail centers, and mixed-use developments reflects Beijing’s role as a global economic player.
The Commercial Property Vacancy Rates graph provides insights into the dynamics of Beijing’s commercial real estate market. A lower vacancy rate indicates a competitive market where available commercial spaces are swiftly occupied, reflecting sustained demand.
Challenges and Opportunities in Beijing’s Real Estate Landscape
While Beijing’s real estate market has shown resilience and adaptability, it faces its fair share of challenges. Housing affordability remains a pressing issue, particularly for young professionals and migrant workers. Striking a balance between meeting the housing needs of the growing population and preventing speculative bubbles poses an ongoing challenge for policymakers.
However, within these challenges lie opportunities for innovation and sustainable development. Beijing has embraced smart city initiatives, green building practices, and mixed-use urban planning, aligning with global trends toward environmentally conscious and technologically advanced urban spaces.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Beijing’s Real Estate
Beijing’s real estate market, a dynamic and multifaceted landscape, mirrors the city’s evolution. As we navigate the intricate interplay of economic forces, government policies, and market dynamics, the graphed trends provide a visual narrative of Beijing’s real estate story.
In conclusion, the future of Beijing’s real estate market hinges on a delicate balance between meeting the demands of a modern, urbanized society and preserving the city’s rich cultural heritage. The resilience and adaptability exhibited by the market, coupled with strategic government interventions, position Beijing as a model for sustainable and vibrant urban development.
The graphed data serves as a roadmap, guiding investors, policymakers, and residents through the twists and turns of Beijing’s real estate landscape. As the city continues to shape its future, the real estate market stands as a testament to Beijing’s unwavering commitment to progress, innovation, and a harmonious blend of tradition and modernity.









