The major equity indices are up 1%-3% over the last week, while 2-year Treasury yields mostly hovered around 3.9%, as economic and bank sector data support the market’s expectation that the Federal Reserve will pause its rate hike cycle.
Historically, the Fed has raised interest rates to combat inflation and lowered them to stimulate economic growth. In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the Fed cut interest rates to near zero in March 2020 and has signaled that it plans to keep rates low until the economy recovers.
In addition to the Fed’s actions, other factors that could impact US interest rates include:
- Inflation: If inflation rises, the Fed may raise interest rates to combat it.
- Economic growth: If the US economy grows faster than expected, the Fed may raise interest rates to prevent overheating.
- International events: Changes in global economic conditions or political events can impact US interest rates.
- Government debt: The level of US government debt and the demand for US Treasuries could also impact interest rates.
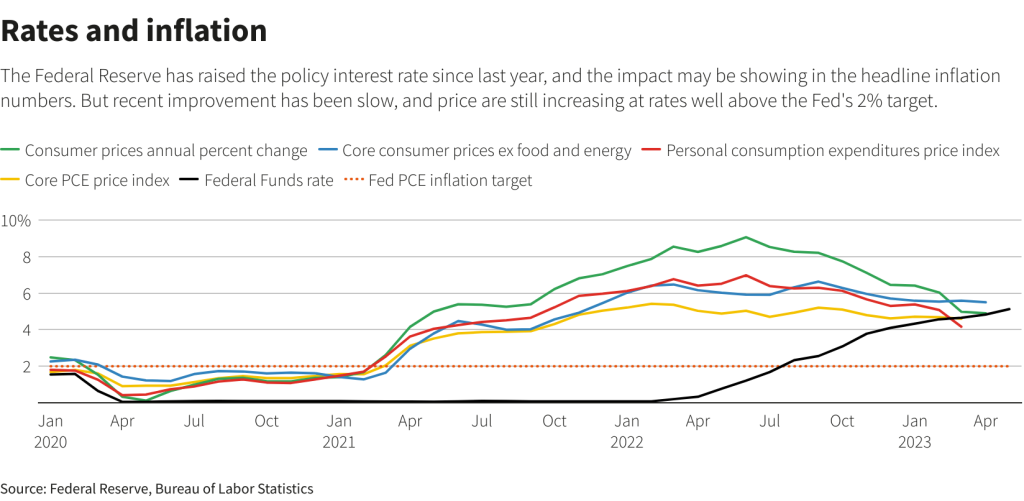
On Friday, the jobs report showed the economy adding 253,000 jobs, and the unemployment rate fell back to 3.4% in April. However, revisions erased 149,000 in job gains from February and March, indicating that the recent pace of job gains has slowed, which should help the Fed’s goal to ease wage inflation by reducing labor demand.
Then, yesterday’s CPI report showed inflation slowing for the tenth consecutive month, as headline CPI inflation fell to 4.9% p.a. Importantly, core services inflation, which has been a concern for the Fed since it tends to be “stickier” than goods inflation, slowed for the second consecutive month to 6.8% p.a. from a peak of 7.3% as housing and wage-driven components both contributed to the decline.
The Fed has also been monitoring the extent to which the recent banking crisis tightens credit availability since a sharp pullback could slow the economy more than desired. The Fed’s latest bank survey saw credit availability tighten less than feared, but standards are already about as tight as around past recessions. For now, though, data on actual lending show that small banks have increased lending each week in April, after two weeks of declining lending immediately following the collapse of Silicon Valley Bank.
So, with continued cooling in the labor market and inflation, alongside some normalization of the banking sector, markets see around a 90% chance the Fed will leave rates unchanged in June.
US Interest Rates and Bitcoin: Understanding the Relationship
The relationship between US interest rates and Bitcoin is a complex one, as it involves many factors that can impact both the US economy and the cryptocurrency market. As the US Federal Reserve adjusts interest rates to manage economic growth and inflation, Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are affected in various ways.
One way in which US interest rates can impact Bitcoin is through the so-called “opportunity cost” of investing. When interest rates are low, it becomes less attractive for investors to hold cash and bonds, as they are likely to earn low returns. This can lead investors to seek out riskier assets, such as stocks and cryptocurrencies, in the hopes of earning higher returns.
Conversely, when interest rates are high, investors may choose to hold cash and bonds instead of riskier assets, as the potential returns from those investments are higher. This can lead to a decrease in demand for Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
Another way in which US interest rates can impact Bitcoin is through the overall state of the economy. When interest rates are low, it can stimulate economic growth, which can be positive for Bitcoin and other riskier assets. On the other hand, if interest rates are raised to combat inflation, it can slow economic growth, which may be negative for Bitcoin.
The impact of US interest rates on Bitcoin is also influenced by other factors, such as government policies, geopolitical events, and technological developments. For example, the recent adoption of Bitcoin as legal tender in El Salvador has sparked interest in the cryptocurrency, leading to a rise in its value, regardless of US interest rates.
Furthermore, Bitcoin is known for its decentralized nature and its lack of correlation with traditional financial markets, which means that its value can fluctuate independently of US interest rates.
Overall, the relationship between US interest rates and Bitcoin is complex and multifaceted. While low interest rates can stimulate demand for Bitcoin, high interest rates can decrease demand for the cryptocurrency. However, other factors such as government policies, geopolitical events, and technological developments can also impact the value of Bitcoin.
Investors who are considering investing in Bitcoin should be aware of the risks involved, as the cryptocurrency market can be highly volatile. It is important to do thorough research and consult with a financial advisor before making any investment decisions.
In conclusion, while US interest rates can have an impact on the value of Bitcoin, investors should take a holistic approach to understand the full range of factors that can impact the cryptocurrency market.









